- Myoelectric Control:
- Myoelectric prosthetic arms are controlled by electrical signals generated by the muscles in the residual limb.
- Electrodes placed on the skin detect muscle contractions, allowing users to control the movement of the prosthetic.
- Neural Interfaces:
- Some advanced prosthetics use neural interfaces, connecting directly to the user’s nerves for more intuitive and natural control.
- Brain-machine interfaces (BMI) or peripheral nerve interfaces (PNI) can be employed to interpret the user’s intentions.
- Bionic Hands:
- Advanced prosthetic hands are designed to mimic the dexterity and functionality of natural hands.
- They may feature individually controllable fingers, allowing for a more precise and versatile grip.
- Sensory Feedback:
- The incorporation of sensory feedback systems provides users with a sense of touch and pressure, improving their ability to interact with objects.
- Tactile sensors on the prosthetic hand can send signals to the user’s nervous system, creating a more immersive experience.
- Advanced Materials:
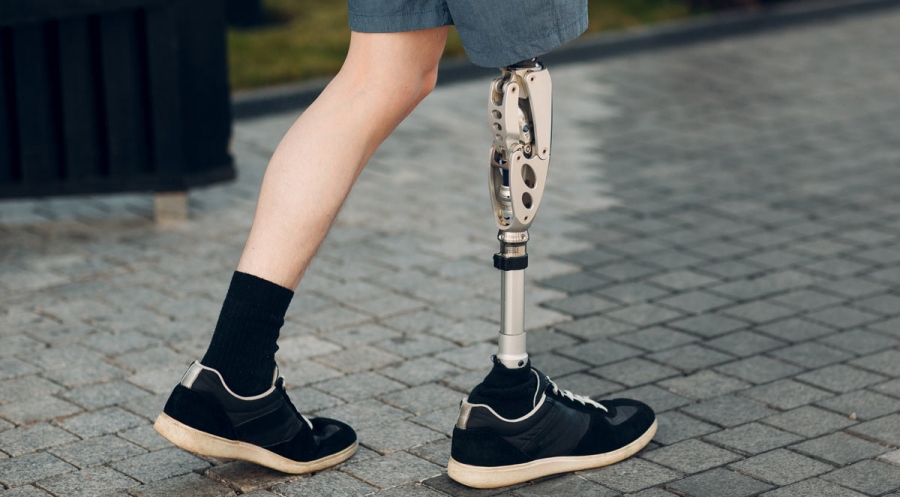
- Lightweight and durable materials, such as carbon fiber and titanium, are often used to construct the prosthetic limb, making it more comfortable for daily use.
Contact with Us – Now
- Lightweight and durable materials, such as carbon fiber and titanium, are often used to construct the prosthetic limb, making it more comfortable for daily use.
- Customization and Personalization:
- 3D printing technology enables the creation of customized prosthetic limbs tailored to the user’s anatomy and preferences.
- Personalization can also extend to the appearance of the prosthetic, allowing users to choose designs or coverings that suit their style.
- Extended Battery Life:
- Advanced batteries and power management systems extend the prosthetic’s battery life, reducing the frequency of recharging.
- Machine Learning and AI:
- Prosthetic arms can leverage machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to adapt and learn from the user’s movements over time, optimizing performance.
- Waterproof and Weather-resistant Design:
- Some prosthetic arms are designed to be waterproof, allowing users to use them in various environments, including the shower or while swimming.
- Bluetooth Connectivity:
- Integration with smartphones and other devices through Bluetooth technology enables additional control options and data tracking.
- Clinical Monitoring:
- Prosthetic arms may include sensors for clinical monitoring, providing healthcare professionals with valuable data on usage patterns and the user’s overall health.
As technology advances, prosthetic arms are likely to become even more sophisticated, offering greater functionality and improved integration with the human body.
Read Also – What are most Prosthetic Limbs made of?